Word Code
Navigating Between Comments
We were asked to write a small tool for someone who wanted to be able to see each user's comments within a Word document and to be able to navigate between the comments. This code, which resides in a start-up Word template, is a more friendly version of the F5 'go to...' function within Word. More importantly, with a little more work we can expand on this tool to manage the comments.
In the current version the user can click on the icon in the toolbar and if a document is present and it has comments then a dialog box appears:
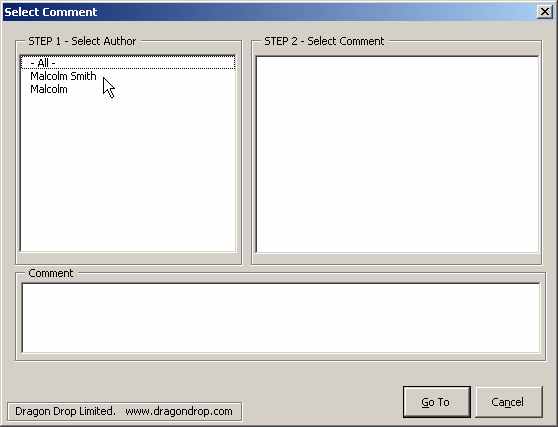
The user is able to select which author's comments to view; or to view all of the comments within the document.
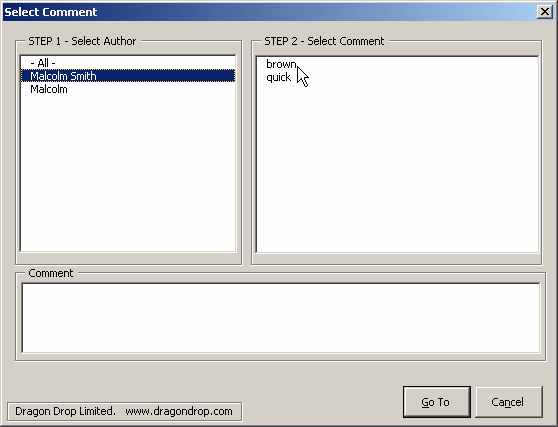
Having selected an author the list of his or her comments are listed in the right hand control.
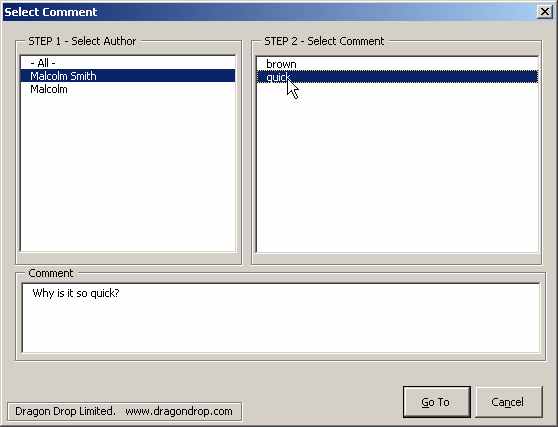
Selecting a comment will do two things. First it will put the actual commment text into the bottom control of the dialog box and, second, the comment within the document will be selected. Therefore, if the user clicks on the 'Go To' button then that comment will remain selected. Clicking on the 'Cancel' button will cause the user's selection to return to where he or she was before this dialog box was brought up.
The code comes in two classes; the modComments code module and the form itself, which is frmSelectComment
The code for the module modComments:
Option Explicit
Public Const ALL_AUTHORS As String = "- All -"
'
Public Sub GoToComment()
Dim oFrm As frmSelectComment
On Error GoTo Error_GotoComment
If Documents.Count > 0 Then
If ActiveDocument.Comments.Count = 0 Then
MsgBox "There are no comments are in the current Active Document.", _
vbOKOnly + vbExclamation, "Dragon Drop Comments"
Else
ActiveDocument.Bookmarks.Add "DragonDropOriginalPosition", Selection.Range
Set oFrm = New frmSelectComment
oFrm.Tag = "Cancel"
oFrm.Show
'--------
If oFrm.Tag = "Cancel" Then
ActiveDocument.Bookmarks("DragonDropOriginalPosition").Range.Select
End If
ActiveDocument.Bookmarks("DragonDropOriginalPosition").Delete
Unload oFrm
Set oFrm = Nothing
End If
End If
Exit_GoToComment:
Exit Sub
Error_GotoComment:
On Error Resume Next
If ActiveDocument.Bookmarks.Exists("DragonDropOriginalPosition") Then
ActiveDocument.Bookmarks("DragonDropOriginalPosition").Range.Select
End If
ActiveDocument.Bookmarks("DragonDropOriginalPosition").Delete
Resume Exit_GoToComment
End Sub
The entry point for the code is the public subroutine, GoToComment(), above. This is what is called from the button on the toolbar.
The code for the form frmSelectComment:
Option Explicit
'
Private Sub cmdCancel_Click()
Me.Tag = "Cancel"
Me.Hide
End Sub
Private Sub cmdGoTo_Click()
Me.Tag = "OK"
Me.Hide
End Sub
Private Sub UserForm_Initialize()
Dim oComment As Comment
Dim sAuthor As String
Me.lstAuthors.AddItem ALL_AUTHORS
For Each oComment In ActiveDocument.Comments
sAuthor = Trim$(oComment.Author)
If Len(sAuthor) > 0 Then
If Not IsAuthorListed(sAuthor) Then
Me.lstAuthors.AddItem sAuthor
End If
End If
Next oComment
End Sub
Private Function IsAuthorListed(sAuthor As String) As Boolean
Dim nIndex As Long
Dim bIsFound As Boolean
bIsFound = False
nIndex = 0
Do While nIndex < Me.lstAuthors.ListCount
If Me.lstAuthors.List(nIndex) = sAuthor Then
bIsFound = True
Exit Do
End If
nIndex = nIndex + 1
Loop
IsAuthorListed = bIsFound
End Function
Private Sub lstAuthors_Click()
Dim nIndex As Long
Dim sAuthor As String
Dim oComment As Comment
Me.lstComments.Clear
Me.txtComment.Text = ""
nIndex = Me.lstAuthors.ListIndex
If nIndex >= 0 Then
sAuthor = Me.lstAuthors.Text
For Each oComment In ActiveDocument.Comments
If oComment.Author = sAuthor Or sAuthor = ALL_AUTHORS Then
Me.lstComments.AddItem oComment.Index
Me.lstComments.List(Me.lstComments.ListCount - 1, 1) = oComment.Scope.Text
End If
Next oComment
End If
End Sub
Private Sub lstComments_Click()
Dim nCommentIndex As Long
Dim nIndex As Long
nIndex = Me.lstComments.ListIndex
If nIndex >= 0 Then
nCommentIndex = Val(Me.lstComments.List(nIndex, 0))
If nCommentIndex > 0 Then
Me.txtComment.Text = ActiveDocument.Comments(nCommentIndex).Range.Text
ActiveDocument.Comments(nCommentIndex).Scope.Select
End If
End If
End Sub
This code is rather straightforward. When the GoToComment() routine is entered the first thing that happens is that the number of open documents are counted. If there are no documents open then nothing happens as the first If...Then statement fails.
The next check is to see if there are any comments within the current active document. This is done by counting the number of .Comments in the ActiveDocument. If there are no comments then the user is informed of this by a message box and then the processing stops.
The next thing that happens is that a bookmark is created in the document at the current selection position and range. This is so that the user can return to this point if he or she presses the Cancel button on the dialog box.
The next thing is that the dialog box is created and before the dialog box is displayed the .Tag property of the dialog box is set to "Cancel". The reason that this is done this way is that one way of processing the result of the button presses on the form is within the form itself or it can be done, as in this example, in the calling routine. The advantage of doing it this way is that if the user cancels the form via the 'x' control then we still have the return value of "Cancel" and we can continue clearing up any objects in exactly the same way as if the the form was left in the expected way.
The dialog box is then shown; the processing is done on the form until the form is closed. After the form is closed the form object is destroyed and the pointer to it reset. If the user didn't exit the form by going pressing the 'Go To' button then the range of the our bookmark is reselected and destroyed thus clearing everything up and leaving no sign that this code was ever executed.
So, what happens when the form is created and until it is destroyed?
The first thing is that it does is on initialising the form the string "- ALL -" is added to the lstAuthors list control and then each comment in the active document is accessed to locate each of the names of the authors of the comment; this is done by looking at the .Author property.
This is the then the situation that the user first sees after he or she has clicked on the toolbar button. The list of comment authors are in the left hand control and the dialog box is ready for user operation.
When the user clicks on an author's name the collection of comments is traversed once more and each comment by that author is placed into the right hand control. What one can see in this control is the actual text used in the main document which is commented.
Actually, the code does a little more than this; the right hand control, lstCommments, actually has two columns. The first column of the lstComments control is zero width and it is into here that the index value of the comment is placed. In the second column, the visible column, is the document commented text.
The reason for this is that each item in the .Comments collection has an index. To save further travelling through the comments each time the user selects a comment in the lstComments window the index value is gathered and the acutal comment can be directly accessed from the collection.
When the comment is selected in the lstComments window the range of the text of the comment, i.e. the comment notes, are placed into the control at the bottom and then, finally, the scope of the comment on the document is selected so it seems like the user has 'gone to the comment' by selecting it in the dialog box.
There is nothing really difficult about this code item but that doesn't mean to say that it isn't useful. Of course there will be futher enhancements to it in the future so that full comment control can be given to the user.
This code can be downloaded from here and placed into Word's start-up folder.
Updates or Comments
If there are any suggestions for updates or comments then please drop us a mail at malcolm.smith@dragondrop.com.
